Minor cuts and scrapes are part of almost every child’s childhood and deemed as part of growing up. Minor cuts and scrapes are small tearing or opening in the skin. It is typically caused by an external injury. Although it is not considered a medical emergency, it is generally advised to give proper first aid care even to minor cuts and scrapes to these small injuries to avoid infections and other complications from developing. Fortunately, most of these can be treated at home. To learn more about treating wounds, register to join First Aid Courses.
Causes of Minor Cuts and Scrapes
The causes of minor cuts and scrapes are typically external injuries that do not cause serious harm to the individual. The common causes include:
- Falling or tripping and hitting a sharp object
- Broken glasses
- Razor cuts
Signs and Symptoms of Minor Cuts and Scrapes
It is typically very evident when an individual has minor cuts and scrapes:
- Small opening or tearing in the skin
- Slight bleeding
- Drainage of small amount of fluid
- Pain
Although minor cuts and scrapes are generally not something to be worried about, every individual, especially parents and guardians, should be on the lookout for signs of infection. The following are signs of infections to look out for:
- Redness, warmth, or swelling in the affected area
- Pus or discharge coming from the cut or scrape
- Fever
- Increased pain
First Aid Treatment of Minor Cuts and Scrapes
The following is the general recommended guidelines to help treat and manage minor cuts and scrapes:
- Although minor cuts and scrapes typically stop bleeding on their own, in cases they do not stop bleeding, gently apply pressure using a clean cloth or bandage. Keep the pressure steady for 20 to 30 minutes. Elevate the wound if possible.
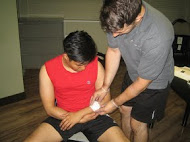
minor cuts and scrapes should be covered with bandages - Clean the wound with clear water. Use soap around the wound but not on the actual wound to avoid irritation. Use tweezers to remove the dirt or debris remaining in the wound. If debris remains, seek medical advice.
- After cleaning the wound, apply a thin layer of antibiotic cream or ointment to keep the surface moist. This will help avoid infection.
- Cover the wound with a bandage to keep harmful bacteria out of the wound. Once there is enough healing, do not put anymore bandage to expose the wound to the air to promote wound healing.
- Change the dressing at least once a day or whenever it becomes wet or dirty.
- Get a tetanus shot to be sure.
Minor cuts and wounds are small tearing or opening in the skin that would require first aid treatment to help avoid complications from developing.
Online Sources:
http://www.mayoclinic.org/first-aid/first-aid-cuts/basics/art-20056711